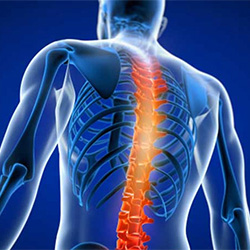
The surgery performed to remove a portion of bone from the posterior aspect of the vertebra (lamina) is known as laminectomy. It is also done in order to remove the bone spurs in the spine. It is minimally invasive, requiring only small skin incisions. Usually, laminectomy is done to treat a condition called spinal stenosis in which the spinal canal becomes narrow and compresses the spinal cord or nerves.
The doctor may suggest laminectomy for you if you have symptoms such as:
- 1. Numbness or pain in one or both legs
- 2. Heaviness or weakness in the legs or buttocks
- 3. Problems while controlling or emptying the bowel or bladder
- 4. Symptoms will be more visible or worsen while you stand or walk
Surgery:
The procedure starts with general anesthesia. After making incisions, the muscles, ligaments and skin are moved to the side. The surgeon will look inside your back by using a microscope. He/she will remove a part or all of the lamina bone on one or both sides of the spine. Small disk fragments, other soft tissues or bone spurs will be removed after that. The surgeon may also do foraminotomy during the surgery, in order to widen the opening where the nerve roots exit from the spine.
Post-surgery
After the surgery, the patient is advised to wear protective brace and mobilize with support. Most probably, the patient can leave the hospital on the 2nd day of surgery. He/She will be able to do light physical activities after four weeks.